A Pedodontics | Paediatric Dentistry Assessment is a clinical evaluation focused on the oral health, development and dental habits of children.
It includes a gentle examination of the teeth, gums and bite. Dentists review brushing habits, nutrition and dental readiness. They also consider a child’s emotional comfort during care. The aim is to guide families, not to promise specific outcomes. Treatment suitability depends on each child’s needs, development and cooperation level.
Pedodontics
Pediatric Dentistry
Common Symptoms / When It May Be Needed
Parents may seek assessment when their child experiences tooth pain, visible decay or sensitivity. Some children complain of chewing discomfort or show difficulty maintaining oral hygiene. Symptoms vary from child to child. An assessment may be helpful when baby teeth fall out early or when adult teeth erupt irregularly. It may also be needed for children who grind their teeth, breathe through the mouth or struggle with dental anxiety. Regular assessments support healthy development and early detection.
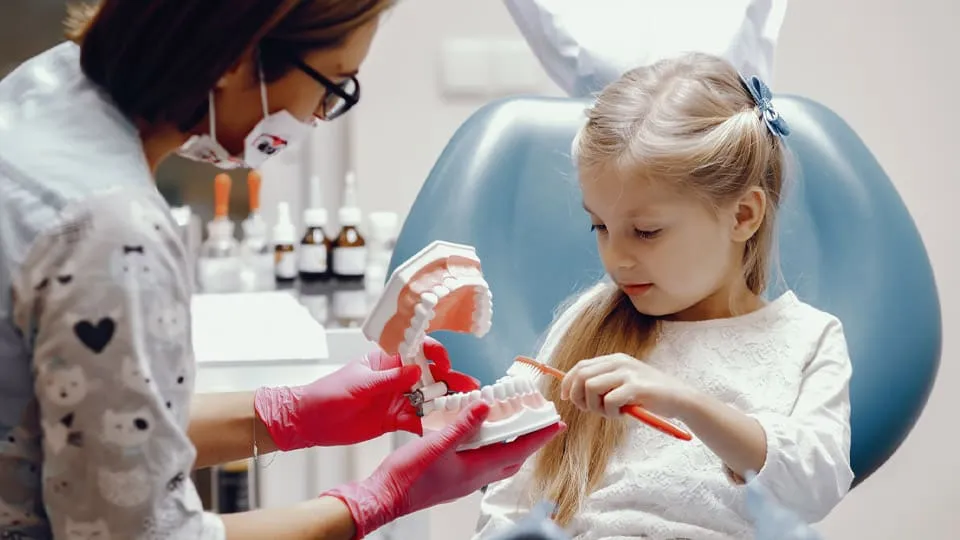

Causes & Risk Factors
Paediatric dental issues may arise from diet, oral hygiene habits, tooth structure or lifestyle factors. High sugar intake, frequent snacking or prolonged bottle use may increase decay risk. Genetic factors influence enamel strength. Thumb-sucking or dummy use may affect tooth alignment. Research suggests that mouth breathing or allergies may influence jaw development. Medical conditions, medications or premature birth may also play a role. Your Dentist considers these factors to guide safe management.
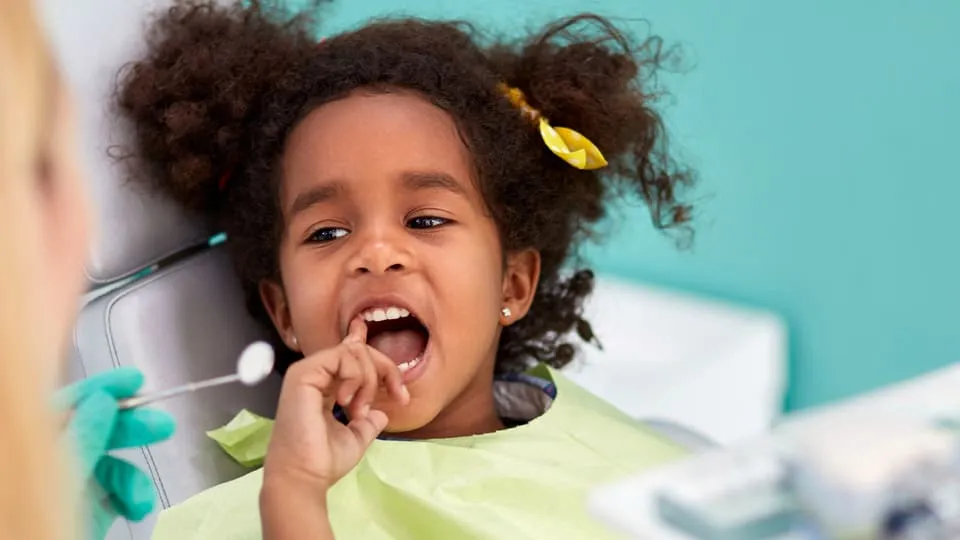

How the Condition is Diagnosed
Diagnosis involves a calm and child-friendly examination. Dentists inspect the teeth for decay, check gum health and assess bite alignment. X-rays may be recommended when needed and are used carefully based on age and safety guidance. Behavioural responses and cooperation levels are also considered. Diagnosis aims to identify both dental health and developmental concerns.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the child’s needs. Options may include fluoride varnish, fissure sealants or simple fillings. Early orthodontic guidance may be offered for bite concerns. Behaviour management techniques help children feel comfortable. When necessary, stainless-steel crowns or pulpotomy treatments may be considered. Children with high anxiety or complex needs may benefit from a referral for sedation. Preventive advice on brushing and diet is always included. Pricing may vary. Please contact the clinic for up-to-date information.
Benefits & Limitations
A paediatric dentistry assessment may help identify early issues and guide healthy habits. Parents often feel reassured after learning how to support their child’s oral health. Early treatment may help improve comfort and prevent complications. However, limitations exist. Children may require multiple visits depending on cooperation. Some conditions develop over time and need ongoing monitoring. No treatment can guarantee permanent results, as growth and habits influence outcomes. Long-term success depends on brushing routines and diet.

Potential Risks & Side Effects
Who is Suitable / Who May Not Be Suitable
Paediatric dentistry services are suitable for most children, including babies, toddlers and teenagers. Children with special educational needs or medical conditions may require additional planning. Some treatments may not be suitable until the child can tolerate specific procedures. Children with uncontrolled medical issues may require GP approval before dental care. Dentists tailor the assessment to the child’s age, behaviour and health.
Aftercare & Recovery Expectations
Aftercare depends on the treatment performed. Children may resume normal activities quickly after most procedures. Mild sensitivity or gum tenderness may occur after fillings or cleaning. Parents are advised to support brushing and avoid sugary snacks. Follow-up visits help monitor healing and development. Good home care plays a key role in long-term stability. Dentists offer guidance on managing discomfort and protecting treated teeth.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Parents should seek dental advice if their child experiences persistent pain, swelling or fever. Sudden tooth fractures or signs of infection require prompt attention. Bleeding that continues or difficulty eating should be evaluated. Mild concerns such as ongoing sensitivity or behavioural issues may be discussed during routine visits.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should my child first see a dentist?
Many Dentists recommend a visit by age one or when the first tooth appears.
Are baby teeth important?
Yes. They support chewing, speech and proper alignment for adult teeth.
Do fillings hurt children?
Dentists use techniques that help manage discomfort, though mild sensitivity may occur afterward.
- This information is intended for general guidance and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your symptoms or treatment options, please consult a qualified healthcare professional.